Remote sensing is a technique of measuring Earth surface features from a distance. It is used in, but not limited to, the fields of geology, geography, seismology, astronomy, archeology, and oceanography. This field encompasses a wide range of techniques, such as aerial photography, passive microwave remote sensing and infrared mapping. This article is a Complete Beginners Guide to What is Remote Sensing and How Does it Work?
What Is Remote Sensing?
Remote Sensing is the study of the acquisition of information about the Earth’s land surface using sensors that are located at a distance from the target area. Remote sensing enables information about the Earth to be gathered and distributed to multiple locations over a distance, without the presence of humans.
Remote sensing has been used for many years in geology and astronomy. In astronomy, astronomers use remote sensing to map the near-infrared spectrum for the purpose of identifying dark clouds, dust, stars, and other celestial objects. The most common method of remote sensing is scanning an entire hemisphere of the Earth at once.
How Does Remote Sensing Work?
Remote sensing starts by acquiring high-resolution data sets for a particular geographic location. These are normally collected and stored in data centers for later analysis and interpretation.
Data from that location is typically displayed on a map, or via satellite imagery. For those data that are unavailable to the public, information about that location is typically stripped from them.
For example, geophysical surveys often remove vegetation data. While those data are replaced by algorithms that map the changes, such as the effects of soil erosion or an earthquake, the stripped data still enable researchers to show changes over time.
What are the different types of Remote Sensing?
There are two types of remote sensing sensors:
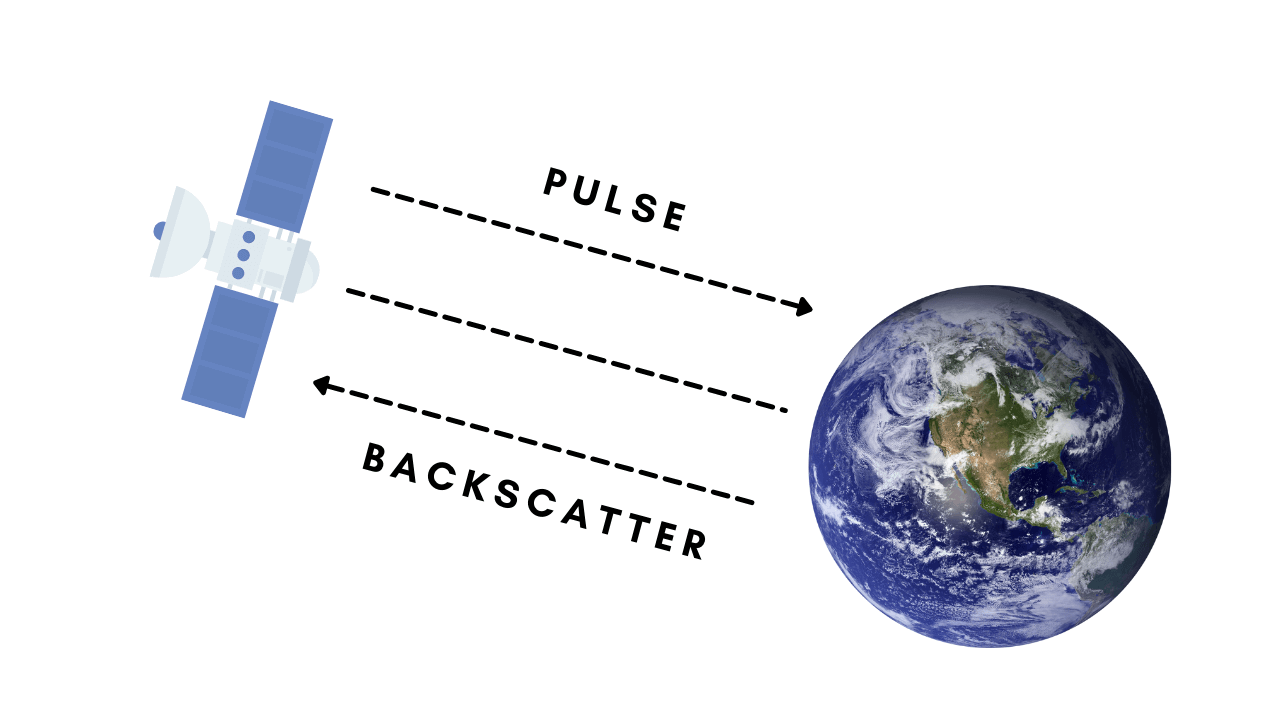
- Active Remote Sensing:
With active remote sensing, the sensors send out microwaves to gather information. The transmitted waves are relatively immune to other weather conditions. Active remote sensing techniques vary depending on what they transmit: light or waves.
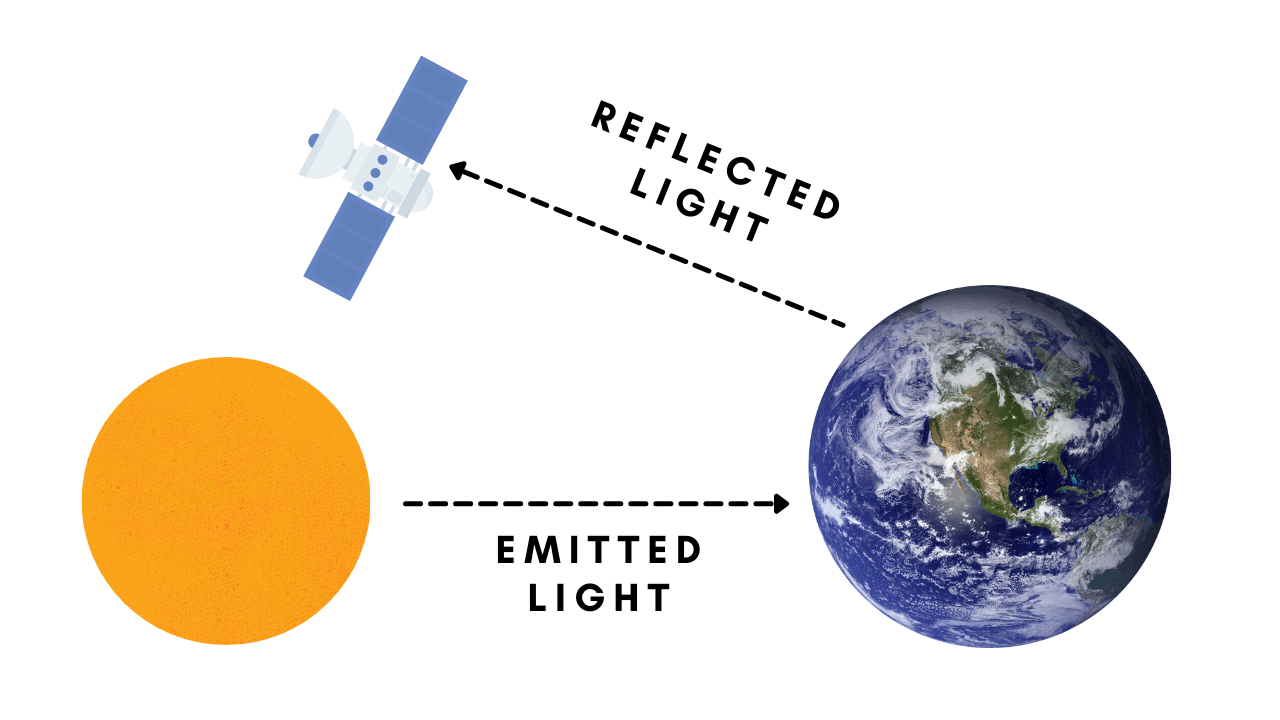
- Passive Remote Sensing:
Passive sensors in remote sensing don’t use their own energy to streamline the researched object. Passive Remote sensing is based on the natural energy (sunrays) that bounce off the target. This means that they can only be applied when there is enough sunlight.
Who Uses Remote Sensing?
Due to the technical capabilities of modern satellites, remote sensing has been used to take images of the Earth and collect other valuable data since the beginning of the 20th century.
Remote sensing is often referred to as airborne remote sensing because of its use by military and civilian air fleets to map and track objects.
Remote sensing is typically performed using specialized satellites that carry sensors to accurately measure a specific feature or attribute of an object or landscape.
Applications of Remote Sensing?
Scientists use remote sensing for a variety of purposes, including:
- Mapping the geologic features of the Earth,
- Creating reliable geographic databases, and interpreting remote sensing data for applications in healthcare, human resources, economics, energy, transportation, and other industries.
- Remote sensing is used in education for several reasons. Students are able to work on spatial data through a variety of projects, including map drawing, statistical analysis, and artistic expression.
- The application of remote sensing can improve the efficiency of various activities, such as transporting goods by land or sea, and be used for the creation of infrastructure to handle natural disasters.
What is Remote Sensing Used For?
Remote sensing technologies are used for two main purposes: the formation of maps and to collect physical characteristics or information, and to better understand the Earth.
In the case of mapping, remote sensing provides information on environmental processes, geographic features, land cover, mineral resources, or human activities.
Remote sensing can also be used to better understand Earth’s geology and climate, and for taking further measurements of the Earth’s environment.
Some of the most common fields where remote sensing is used, including geography, land surveying, geology, hydrology, oceanography, meteorology, ecology, glaciology.
The History of Remote Sensing?
A remote sensing technology developed by the U.S. Air Force. They developed the aerial mapping of Earth from the 1950s-1960s.
Geographer Evelyn Pruitt was the first to invent Remote Sensing with the U.S. Office of Naval Research.
Uses of Remote Sensing
Below are the some Remote Sensing Uses listed:
- Remote sensing is the exploration and study of natural resources and phenomena by collecting information on them from a distance.
- Remote sensing is used to study the earth’s atmosphere, topography, oceans and resources.
- Remote sensing is used by the military, meteorology, agriculture, forestry, environmental protection, etc.
- Remote sensing is also used by researchers to conduct research and collect data from a distance.
Remarks:
There are more than a hundred scientific journals dedicated to the study of remote sensing. Many of these journals are recognized and publish information about remote sensing.