In the realm of geospatial technology and remote sensing, two terms that often come up are LiDAR and DEM. These technologies play crucial roles in various fields, from environmental monitoring to urban planning. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the world of LiDAR and DEM (Lidar Vs DEM) to understand their differences, applications, and the advantages they offer.
LiDAR and DEM differ in data collection methods. LiDAR uses laser pulses for precise 3D measurements, while DEM represents elevation at grid points. LiDAR offers higher accuracy for detailed objects, while DEM serves broader terrain analysis.
Introduction: Unveiling the Acronyms
Before we dive deeper into the comparison, let’s demystify the acronyms.
What is LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging)?
LiDAR, short for Light Detection and Ranging, is a remote sensing technology that uses laser pulses to measure distances between the sensor and the Earth’s surface. It’s like sonar but with laser beams instead of sound waves.
What is DEM (Digital Elevation Model)?
DEM, or Digital Elevation Model, is a 3D representation of a terrain’s surface. It provides information about the elevation of various points on the Earth’s surface and is a crucial component in various applications, including cartography and flood modeling.
| LiDAR | DEM |
|---|---|
| Acquires raw point cloud data | Represents processed elevation information |
| Provides high-resolution, 3D information | Often presented in a 2D raster format |
| Utilizes laser technology | Generated from various data sources including LiDAR |
| Ideal for precise measurements and detailed models | Serves as a foundational layer for GIS applications |
LiDAR vs DEM: The Showdown
Now that we’ve clarified what these acronyms stand for, let’s pit them against each other in a head-to-head comparison.
Data Collection
LiDAR data is collected by sending laser pulses to the ground and measuring the time it takes for them to bounce back. This technology provides highly accurate 3D data, including information about the height of objects on the ground, such as trees and buildings.
DEM data, on the other hand, is derived from various sources, including LiDAR. It represents the elevation of the Earth’s surface at grid points and is usually available at lower resolutions compared to LiDAR data.
Accuracy
LiDAR is renowned for its exceptional accuracy. It can capture minute details with high precision, making it indispensable for applications like autonomous vehicles and forestry management.
DEM, while valuable, may not match LiDAR’s level of accuracy. It serves its purpose in applications where slightly lower precision is acceptable.
Cost
LiDAR data collection and processing can be expensive due to the specialized equipment and expertise required. DEM data, on the other hand, is often more cost-effective, especially when derived from various free or low-cost sources.
Applications
LiDAR finds its applications in various fields, such as:
- Forestry: Assessing tree heights and canopy structures.
- Agriculture: Monitoring crop health and yield estimation.
- Urban Planning: Creating detailed 3D city models.
- Archaeology: Discovering hidden archaeological sites.
DEM is commonly used in:
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): Creating topographic maps.
- Hydrology: Modeling water flow and flood risk assessment.
- Civil Engineering: Planning infrastructure projects.
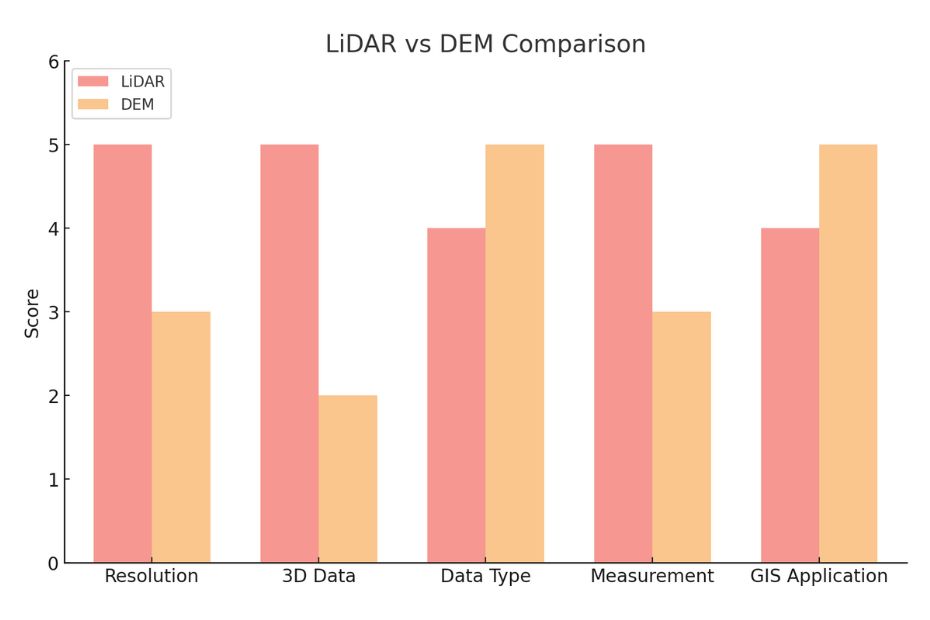
Here is a visual comparison of LiDAR and DEM based on various parameters such as resolution, 3D data representation, data type, measurement accuracy, and application in GIS. The chart provides a score out of 5 for each parameter, illustrating the areas where each technology excels. This can help readers visualize the strengths and limitations of LiDAR and DEM in spatial mapping applications.
Conclusion
In the battle of LiDAR vs DEM, there is no clear winner; both technologies have their strengths and applications. LiDAR shines when precision and detailed 3D data are paramount, while DEM offers a cost-effective solution for broader terrain analysis.
In summary, while both LiDAR and DEMs are used to represent elevation data, they differ in terms of data acquisition, format, and detail level. LiDAR provides highly detailed and accurate point data, which can be used to create DEMs. On the other hand, DEMs offer a gridded, continuous representation of the Earth’s surface, useful for a wide range of applications. The choice between LiDAR data and DEMs, or the integration of both, depends on the specific requirements of the project, including the desired level of detail, accuracy, and the nature of the application.
FAQs: Lidar Vs DEM
How accurate is LiDAR data?
LiDAR data is known for its exceptional accuracy, capable of capturing minute details with high precision.
Can DEM data be derived from LiDAR?
Yes, DEM data can be derived from LiDAR data, among other sources, to represent the elevation of the Earth’s surface.
