In today’s rapidly advancing technological landscape, Lidar has emerged as a game-changing technology, revolutionizing various industries from autonomous vehicles to environmental monitoring. But a question that often arises is, “Does Lidar work in fog?” In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the intricacies of Lidar technology and its performance in foggy conditions.
Yes, Lidar can work in fog, but it faces challenges. Fog reduces visibility and can scatter the laser beam, affecting accuracy. However, advancements like multi-wavelength Lidar and improved algorithms are enhancing its performance in foggy conditions.
Understanding LiDAR Technology
LiDAR, which stands for Light Detection and Ranging, is a remote sensing method that uses light in the form of a pulsed laser to measure distances. This technology creates precise, three-dimensional information about the shape of the Earth and its surface characteristics.
For more insights into the differences between LiDAR and other similar technologies, consider reading about LiDAR vs. Photogrammetry, LiDAR vs. Radar, and LiDAR vs. LADAR.
Does Lidar Work In Fog?
Innovative approaches are being developed to improve LiDAR’s functionality in foggy conditions. One such method involves using different wavelengths of light, which can vary in their ability to penetrate fog.
Additionally, advanced signal processing techniques can help in distinguishing the actual signal from the noise caused by fog. For an understanding of how LiDAR technology operates under different conditions, the article on LiDAR vs. Laser provides valuable insights.
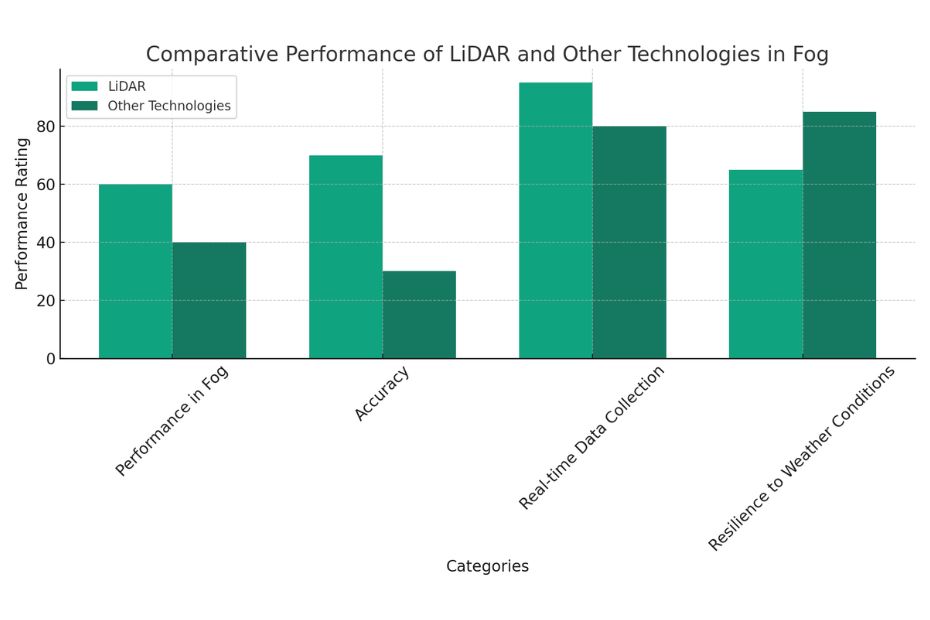
Comparative Analysis: LiDAR vs. Other Technologies in Fog
When it comes to operating in foggy conditions, LiDAR has its limitations compared to other technologies like radar and sonar.
Radar, for instance, uses radio waves which can penetrate fog more effectively. Understanding these differences is essential, especially when considering applications that require operation in various weather conditions.
For a deeper understanding, explore the differences and similarities between these technologies through articles like LiDAR vs. Radar and LiDAR vs. Sonar.
The Foggy Challenge
Fog is a meteorological phenomenon that consists of tiny water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air. When Lidar technology encounters fog, several challenges arise:
Reduced Visibility
Fog significantly reduces visibility by scattering and absorbing light. Lidar systems rely on the laser beam’s reflection, but in fog, the beam can be scattered in various directions, making it difficult to obtain accurate distance measurements.
Signal Interference
Fog can cause signal interference, leading to inaccuracies in Lidar data. The scattered light from fog particles can confuse the sensor, resulting in false readings or incomplete scans.
Lidar in Action: Overcoming Fog
Despite the challenges posed by fog, Lidar technology has made significant strides in overcoming these obstacles. Here’s how:
1. Multi-Wavelength Lidar Systems
Modern Lidar systems often utilize multiple wavelengths of light. By using different wavelengths, Lidar can penetrate fog more effectively. Shorter wavelengths are scattered less by fog, allowing Lidar to gather more accurate data.
2. Improved Algorithms
Sophisticated algorithms are employed to filter out noise and distortions caused by fog. These algorithms analyze the data collected by Lidar and enhance its accuracy, even in adverse weather conditions.
3. Higher Pulse Rates
Higher pulse rates mean more laser pulses are sent out per second. This increased density of data points allows Lidar to capture a more detailed picture of the environment, compensating for any loss of data due to fog.
Real-World Applications
Now that we understand how Lidar can combat foggy conditions let’s explore some real-world applications where this technology shines, fog notwithstanding:
Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving cars heavily rely on Lidar to perceive their surroundings. Lidar’s ability to navigate through fog is crucial for the safe operation of autonomous vehicles, ensuring that they can detect obstacles even in adverse weather.
Environmental Monitoring
Lidar is used in environmental monitoring to track changes in landscapes, vegetation, and more. Even in foggy conditions, Lidar can provide valuable data for assessing ecological changes.
Disaster Response
During natural disasters, such as hurricanes or earthquakes, rescue and relief efforts often require detailed mapping of affected areas. Lidar can operate effectively in fog, aiding in these critical missions.
Advancements and Future Directions
The future of LiDAR technology in adverse weather conditions like fog is promising. With ongoing research and development, there are advancements in LiDAR systems that make them more resilient to such challenges.
This includes the development of new types of LiDAR, such as those using different time-of-flight principles. A deeper dive into these technological differences can be found in LiDAR vs. Time-of-Flight (ToF) Sensors.
Key Considerations for Using LiDAR in Fog
Professionals using LiDAR technology must consider several factors when operating in foggy conditions. These include the wavelength of the LiDAR system, the density of the fog, and the specific application requirements.
By understanding these elements, users can better anticipate and mitigate the challenges posed by fog.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, while fog does present challenges for Lidar technology, it is not an insurmountable obstacle. With advancements in multi-wavelength Lidar and improved algorithms, Lidar systems have become more resilient in adverse weather conditions. As a result, Lidar can work effectively in fog, contributing to safer autonomous vehicles and more accurate environmental monitoring.
FAQs: Does Lidar Work In Fog?
Can Lidar technology work in heavy fog?
Yes, with the use of multi-wavelength Lidar and advanced algorithms, Lidar can function reasonably well in heavy fog, although its performance may be slightly compromised compared to clear conditions.
Are there any limitations to using Lidar in foggy conditions?
While Lidar can work in fog, it may experience reduced range and accuracy compared to ideal conditions. Users should be aware of these limitations when deploying Lidar technology in foggy environments.
How does Lidar compare to other sensing technologies in fog?
Lidar has advantages over some other sensing technologies, such as radar, in foggy conditions because it relies on laser beams that can penetrate fog to some extent.
Can Lidar be used for aviation purposes in foggy weather?
Lidar technology is not commonly used for aviation purposes in foggy weather. Aviation relies on other advanced systems for navigation in such conditions.
