In today’s globalized world, the geography of a region plays a pivotal role in shaping its industrial growth. From access to resources and transportation routes to the influence of climate and terrain, geography can significantly impact a nation’s economic development. In this comprehensive article, we delve deep into the question, “How Does Geography Affect Industrial Growth?” and uncover the multifaceted ways in which geography and industry intersect.
Geography profoundly influences industrial growth. Abundant natural resources, accessible transportation routes, and favorable climates can stimulate economic development. Conversely, challenging terrain or extreme climates may require innovative solutions. Understanding these geographical dynamics is key to shaping successful industrial strategies.
Introduction: How Does Geography Affect Industrial Growth?
The influence of geography on industrial growth is a multifaceted and dynamic subject. Understanding this influence is crucial for comprehending the evolution and distribution of industrial activities across the globe. This article delves into various aspects of how geography impacts industrial growth, highlighting the role of transport technology, climate, and historical industrial revolutions.
Evolution of Transport Technology and Industrial Growth
The evolution of transport technology plays a pivotal role in shaping the geography of growth and development. Changes in transportation have historically enabled access to new resources, markets, and have facilitated the diffusion of general-purpose technologies. This evolution has led to significant shifts in economic structures, transitioning from agricultural bases to manufacturing and service-oriented economies.
Geography’s Direct and Indirect Impact on Growth
Geography’s relationship with macroeconomic growth is intricate. It influences growth both directly and indirectly, affecting economic policies and institutional frameworks. These elements are critical as they shape the environment in which industries operate and grow. Geographic factors also have a direct impact on the choices of policies and the nature of institutions, further underscoring their importance in industrial development.
Climate and Long-Term Development
The impact of climate and geography on long-term development, though indirect, is significant. It influences the organization of societies, which in turn affects industrial activities and growth. The way societies are structured, their resource management, and adaptive strategies to their geographical settings have profound implications for industrial growth and sustainability.
Influence of Location on Economic Growth
Location and climate exert a substantial impact on income levels and economic growth. Factors such as transport costs, disease burdens, and agricultural productivity are all influenced by geographical location. This means that regions with favorable geographic conditions are more likely to experience accelerated industrial growth compared to those with less conducive environments. Furthermore, geography influences economic policy decisions, which are critical for industrial development.
Historical Perspective: Industrial Revolutions and Geography
The global geography of innovation and industrial development has been significantly shaped by historical industrial revolutions. Each major industrial revolution introduced unique geographical patterns of development and income distribution. Understanding these historical trends is essential for comprehending the current geographical distribution of industrial activities and the potential for future growth.
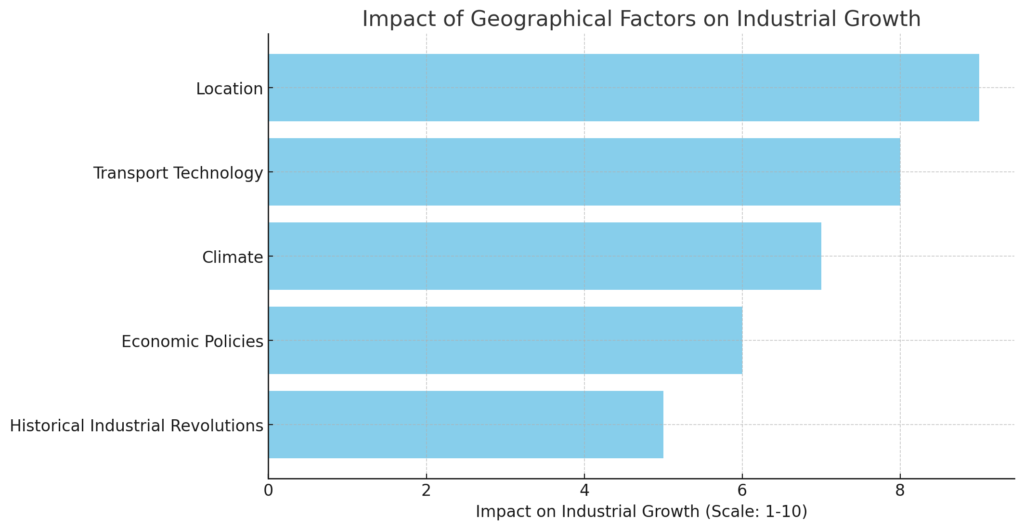
Some of the key of geography that contribute to or hinder industrial growth:
| Factor | Impact on Industrial Growth |
|---|---|
| Transport Technology | Evolution in transport technology shapes industrial growth by altering access to resources and markets. |
| General-Purpose Technologies | Diffusion of these technologies leads to structural transformations in economies. |
| Economic Policies and Institutions | Geography influences economic policy choices and the framework of institutions. |
| Climate | Affects long-term development by shaping social organization and resource availability. |
| Location | Influences income levels and growth through transport costs, disease burdens, and agricultural productivity. |
| Historical Industrial Revolutions | Each revolution brought distinctive geographical development patterns, affecting income distribution. |
Conclusion:
Geography is a silent yet powerful force in the world of industrial growth. By recognizing the influence of location, climate, terrain, and other geographical factors, regions can strategically position themselves for economic development. From the availability of resources to the impact of climate change, geography weaves a complex tapestry that shapes industrial growth across the globe.
FAQs: How Does Geography Affect Industrial Growth?
Can a region with adverse geographical conditions experience industrial growth?
Yes, with the right infrastructure and strategic planning, even regions with challenging geography can experience industrial growth.
How can a region leverage its geographical location for industrial development?
Proximity to transportation hubs and consumer markets can be leveraged to attract industries. Investment in infrastructure is key.
What role does climate play in industrial growth?
Climate influences the types of industries that thrive in a region and impacts energy production choices.
Is a skilled workforce more readily available in urban or rural areas?
Urban areas tend to have a larger pool of skilled workers, making them attractive for industries.
