Geography plays a significant role in shaping the distribution and growth of human populations around the world. The interaction between people and their environment is a complex and multifaceted one. In this article, we will explore how does geography affect population? From the impact of climate and topography to access to resources and transportation networks, we will delve into the intricacies of this relationship.
Geography significantly impacts population distribution. Climate, topography, and resource availability shape where people live. Coastal areas attract due to trade, while harsh climates can deter large populations. Understanding these factors is key to comprehending population dynamics.
How Does Geography Affect Population?
Geography is not just about mountains, rivers, and maps; it significantly shapes the distribution, density, and growth of human populations. Let’s embark on a journey to understand how geography influences where people live and why.
Urban vs. Rural
One of the fundamental ways geography affects population is by influencing urbanization and rural settlement patterns. Coastal areas tend to attract larger urban populations due to trade opportunities, while inland regions often favor rural lifestyles.
Coastal vs. Inland
Coastal areas have long been attractive to urban populations due to the economic opportunities they offer. Proximity to the sea facilitates trade, commerce, and access to international markets. Coastal cities often become bustling hubs of activity, drawing people seeking employment and business prospects. Furthermore, the scenic beauty and temperate climate of coastal regions provide an attractive living environment.
In contrast, inland regions may present harsher climates and fewer economic incentives. The lack of access to the sea can limit trade opportunities and the development of urban centers. As a result, these areas tend to favor rural lifestyles, where agriculture and resource-based livelihoods are more common.
Climate and Population
The climate of a region is a pivotal factor influencing population distribution. Regions with moderate climates are generally more densely populated. Mild temperatures, ample rainfall, and predictable weather conditions are conducive to human settlement. Extreme weather conditions, such as severe cold or scorching heat, can deter people from living in certain areas.
Natural Resources and Population Centers
Agriculture and Fertile Land
Geographical regions blessed with fertile soil and abundant water sources tend to support large agricultural populations. The availability of fertile land and water for irrigation has historically played a crucial role in the growth of civilizations. Riverbanks and fertile valleys have been the cradle of human societies, enabling agriculture to thrive and support dense populations.
Water Resources
The availability of freshwater is a critical determinant of where human settlements thrive. Communities tend to cluster around rivers, lakes, and other freshwater sources as these are essential for drinking, irrigation, and industrial purposes. The presence of freshwater ensures the survival and prosperity of populations.
Topography and Population Density
Mountains and Plateaus
Mountainous terrain and plateaus often have lower population densities. Rugged landscapes make agriculture and infrastructure development more challenging. The steep slopes and lack of arable land limit the possibilities for large urban centers, leading to sparser populations in these regions.
Plains and Valleys
In contrast, plains and valleys provide favorable conditions for agriculture and urbanization. These areas have fertile soil, relatively flat topography, and access to water, making them ideal for settlements and the growth of dense populations.
Historical Perspectives
Ancient Civilizations
Ancient civilizations like Mesopotamia and Egypt thrived in fertile river valleys. The geographical features of these regions, particularly the Tigris and Euphrates in Mesopotamia and the Nile in Egypt, played a pivotal role in the birth and development of these early human societies. The annual flooding of these rivers replenished the soil, making it exceptionally fertile for agriculture. This abundance of resources allowed for the sustenance of large populations and the establishment of advanced civilizations.
Colonial Expansion
Colonial powers in history strategically exploited geography for their benefit. They established colonies in regions with abundant natural resources, access to trade routes, and favorable climates. This exploitation of geography allowed colonial empires to extract wealth and resources from their colonies, influencing population patterns and urbanization in these areas. The legacies of colonialism continue to impact the population distribution and socio-economic conditions of many countries today.
Migration Patterns
Push and Pull Factors
Geography is a key driver of migration patterns. People often migrate due to a combination of push and pull factors influenced by geographical conditions. Push factors may include unfavorable environmental conditions such as droughts, floods, or natural disasters, as well as political instability or conflict in a region. Pull factors, on the other hand, can be geographical advantages such as access to fertile land, job opportunities, and better living conditions in more geographically advantageous areas.
Forced vs. Voluntary Migration
Geographical factors can lead to both forced and voluntary migrations. Forced migrations occur when people are compelled to leave their homes due to environmental disasters like hurricanes, earthquakes, or flooding, or due to conflict and persecution. Voluntary migrations, on the other hand, are driven by individual or collective choices, often influenced by the geographical advantages of a new location.
Modern Geographic Influences
Technology and Connectivity
In the modern world, advances in technology have reduced the significance of geographical barriers. The internet, transportation networks, and communication technology have made it possible for people to live in remote areas while remaining connected to the global economy. This has led to the rise of telecommuting and digital nomadism, where individuals can work and live in locations of their choosing, regardless of geographical constraints.
Environmental Factors
Environmental issues, such as rising sea levels and the increasing frequency of natural disasters, are having a profound impact on population distribution. Coastal regions are particularly vulnerable to rising sea levels, leading to the displacement of populations. Additionally, the increased occurrence of extreme weather events can force people to migrate to safer geographical locations.
Challenges and Solutions
Overpopulation
Overpopulation in certain geographic regions can place immense strain on resources and infrastructure. Issues such as overcrowding, pollution, and resource scarcity become more pronounced in densely populated areas. To address these challenges, innovative solutions are needed, including sustainable urban planning, resource management, and population control measures.
Depopulation
Conversely, depopulation in remote or economically challenged areas can lead to social and economic issues. Reduced populations can result in a decline in economic activity, limited access to services, and the aging of communities. To combat depopulation, efforts may be directed toward creating incentives for people to live and work in these areas, including economic development initiatives and improved infrastructure.
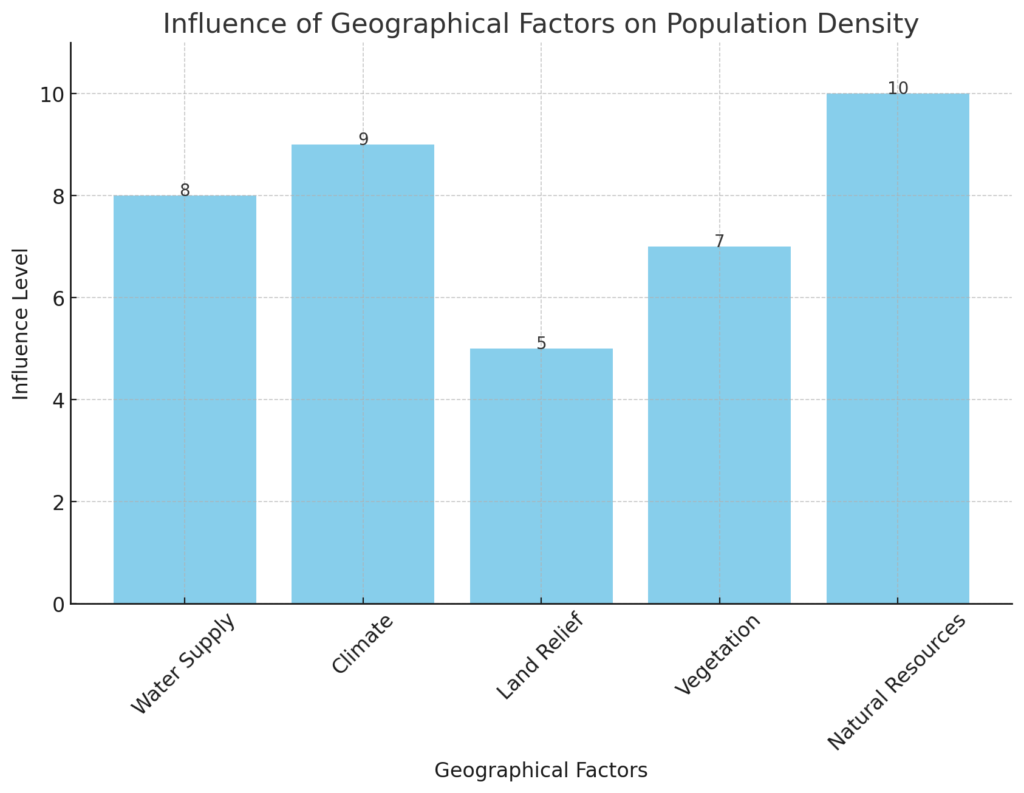
Physical Factors Influencing Population Density
- Water Supply: Essential for life, water sources like rivers and lakes attract settlements.
- Climate: Regions with temperate climates are often more densely populated.
- Land Relief: Mountainous or difficult terrain can deter dense populations.
- Vegetation: Areas with fertile land, suitable for agriculture, often have higher population densities.
- Natural Resources and Energy: Regions rich in resources like minerals or oil tend to attract more people.
These factors don’t just determine where people live; they also influence how societies develop and grow.
For instance, a city near a water source may become a trade hub, while a region with fertile land might develop a strong agricultural economy.
Urbanization and Geographic Distribution
Urbanization, the process of population shifting from rural to urban areas, is significantly influenced by geography. The value of land in different regions, for its agricultural potential or other purposes, dictates population density. Some areas may be sparsely populated due to their limited agricultural value, while others, with rich resources, become densely populated urban centers.
Resources and Population Growth
The relationship between population and resource availability is reciprocal. As the population grows, the demand for resources increases, affecting the earth’s surface and natural systems.
Conversely, the availability of resources can also fuel population growth, as seen in areas where technological advancements have expanded the human ecumene – the habitable part of the earth’s surface.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, geography is a powerful force in shaping the world’s population patterns. From the distribution of natural resources to the terrain’s shape, these factors collectively influence where and how we live. Understanding this relationship is crucial for addressing challenges related to urbanization, resource management, and environmental sustainability.
FAQs: How Does Geography Affect Population?
Can geography alone determine a region’s population?
No, geography is just one of many factors that influence population. Socioeconomic, cultural, and political factors also play significant roles.
Are coastal areas always densely populated?
While coastal areas often have high population densities, this is not a universal rule. Factors like infrastructure and economic opportunities also matter.
How does climate change impact population distribution?
Climate change can force people to migrate due to rising sea levels, extreme weather events, or changes in agricultural patterns, affecting population distribution.
What role does technology play in mitigating geographical challenges?
Advancements in technology can help mitigate geographical challenges, such as improved infrastructure for remote areas and disaster preparedness.
Is there a relationship between geography and culture?
Yes, geography can influence cultural practices and traditions, as well as impact language and lifestyle choices in a region.
