Geography is a fascinating subject that deals with the study of the Earth’s physical features, including its shape and size. One important concept that plays a significant role in understanding the Earth’s shape is the Geoid. But what is the Geoid, and why is it essential in geography?
In this article, we will delve into the definition and explore What is Geoid in geography, its importance, and how it relates to the Earth’s shape. We will discuss the methods used to measure the Geoid and its applications in various fields of study. By the end of this article, you will have a better understanding of this crucial concept in geography and its significance in various scientific fields.
What is the Shape of the Earth?
Before we delve into geoid, we need to understand the shape of the Earth. The Earth is not a perfect sphere but is an oblate spheroid. This means that it is flattened at the poles and bulges at the equator. This shape is due to the Earth’s rotation and the centrifugal force acting on it.
What Is Geoid In Geography?
Geoid is defined as an equipotential surface of the Earth’s gravity field that coincides with the mean sea level. It is an imaginary surface that closely approximates the shape of the Earth, taking into account the irregularities in the distribution of mass within the Earth.
Geoid is an imaginary surface that is used as a reference level for measuring elevations on the Earth’s surface. It is used in physical geography and geodesy to determine the height of land and sea levels.
How is the Geoid different from the Earth’s shape?
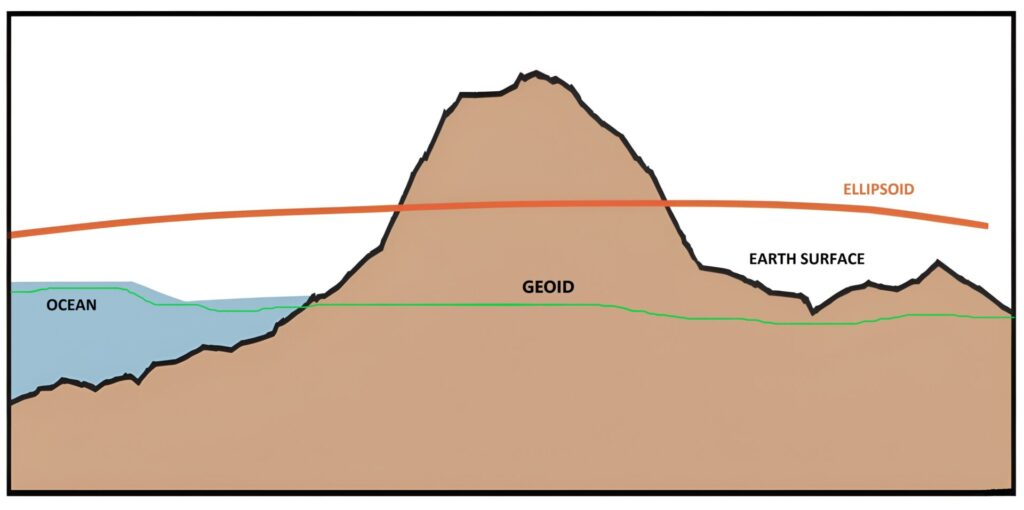
The shape of the Earth is often described as an oblate spheroid, a shape that results from the Earth’s rotation around its axis. This shape is not uniform, and it varies from place to place due to the differences in the distribution of mass within the Earth.
The Geoid takes into account these variations and represents the shape of the Earth as a more accurate and realistic model.
Applications of the Geoid
The Geoid has numerous applications in various fields of study, including:
- Geodesy: The Geoid is used as a reference surface to measure elevations and depths on the Earth’s surface accurately. It is essential for creating accurate maps and determining the shape and size of the Earth.
- Oceanography: The Geoid is used to measure ocean currents and sea level changes. By studying the Geoid, scientists can gain a better understanding of the Earth’s oceans and their impact on climate and weather patterns.
- Geophysics: The Geoid is used to study the Earth’s internal structure and its gravitational field. It is essential for understanding the formation of the Earth and the processes that shape our planet.
- Geolocation: The Geoid is used to provide accurate coordinates for locations on the Earth’s surface. This is essential for navigation and finding locations for various purposes, including scientific research and resource exploration.
- Cartography: The Geoid is used to create accurate maps that take into account the Earth’s shape and size. This is essential for creating detailed maps for various purposes, including navigation, resource exploration, and urban planning.
Overall, the Geoid plays a significant role in various fields of study, from scientific research to practical applications. Its accurate measurement is essential for accurate positioning and navigation, and it will continue to be an essential tool for scientific research and practical applications in the future.
Conclusion
The Geoid is an essential concept in geography that helps us understand the shape of the Earth. It takes into account the variations in the distribution of mass within the Earth and represents the Earth’s shape more accurately than the oblate spheroid model. The Geoid has numerous applications in various fields of study and is an important tool for geodesy, oceanography, geophysics, geolocation, cartography, and navigation.
FAQs:
Why is the Geoid important?
The Geoid is an essential tool for geodesy, the study of the size and shape of the Earth. It is the reference surface used to measure elevations and depths on the Earth’s surface.
What are the applications of the Geoid?
The Geoid has numerous applications in various fields of study, including geodesy, oceanography, geophysics, geolocation, cartography, and navigation. In geodesy, the Geoid is used as a reference surface to measure elevations and depths on the Earth’s surface. In oceanography, the Geoid is used to measure ocean currents and sea level changes. In geophysics, the Geoid is used to study the Earth’s internal structure and its gravitational field. It is also used in geolocation, cartography, and navigation to provide accurate coordinates for locations on the Earth’s surface.
How is geoid different from mean sea level?
Geoid is an imaginary surface that represents the Earth’s shape under the influence of gravity alone, while mean sea level is the average height of the ocean’s surface over time.